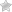FDA记录表明,这种药物目前没有召回。beplay sport中心钱包
Are you a medical professional?
热门话题
Twinrix Recall
Get an alertwhen a recall is issued.
Questions & Answers
Side Effects & Adverse Reactions
肌病/横纹肌溶解
与HMG-COA还原酶的其他抑制剂一样,lovastatin偶尔会导致肌病表现为肌肉疼痛,压痛或无力,肌酸激酶(CK)超过正常上限(ULN)的十倍。肌病有时会采取横纹肌溶解的形式,无论有或没有急性肾脏衰竭,其继发于肌红尿症,并且发生了罕见的死亡。血浆中HMG-COA还原酶抑制活性高水平的风险增加。
The risk of myopathy/rhabdomyolysis与剂量有关。我n a clinical study (EXCEL) in which patients were carefully monitored and some interacting drugs were excluded, there was one case of myopathy among 4933 patients randomized to lovastatin 20 to 40 mg daily for 48 weeks, and 4 among 1649 patients randomized to 80 mg daily.
There have been rare reports of immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy (IMNM), an autoimmune myopathy, associated with statin use. IMNM is characterized by: proximal muscle weakness and elevated serum creatine kinase, which persist despite discontinuation of statin treatment; muscle biopsy showing necrotizing myopathy without significant inflammation; improvement with immunosuppressive agents.
All patients starting therapy with lovastatin, or whose dose of lovastatin is being increased, should be advised of the risk of myopathy and told to report promptly any unexplained muscle pain, tenderness or weakness particularly if accompanied by malaise or fever or if muscle signs and symptoms persists after discontinuing lovastatin. Lovastatin therapy should be discontinued immediately if myopathy is diagnosed or suspected。在大多数情况下,当迅速停止治疗时,肌肉症状和CK会增加。可以在患者使用lovastatin或增加剂量的患者中考虑定期CK测定,但不能保证这种监测会预防肌病。
许多因洛伐他汀治疗而出现横纹肌溶解的患者的病史复杂,包括肾功能不全通常是由于长期存在的糖尿病而导致的。这样的患者值得更近的监测。如果发生明显升高的CPK水平,或者诊断或怀疑肌病,应停止lovastatin疗法。在任何经历急性或严重疾病的患者中,洛伐他汀疗法也应暂时抑制,这易受横纹肌溶解继发的肾衰竭的发展,例如败血症;低血压;大手术;创伤;严重的代谢,内分泌或电解质疾病;或不受控制的癫痫。
The risk of myopathy/rhabdomyolysis is increased by concomitant use of lovastatin with the following:
Strong inhibitors of CYP3A4
与HMG-COA还原酶的其他几种抑制剂一样,lovastatin是细胞色素P450 3A4(CYP3A4)的底物。某些抑制这种代谢途径的药物可以提高lovastatin的血浆水平,并可能增加肌病的风险。这些包括伊曲康唑,酮康唑,寄生虫,伏立康唑,大环内酯类抗生素红霉素和克拉霉素,酮醇蛋白酶抗生素链霉素,HIV蛋白酶抑制剂,Boceprevir,Boceprevir,Boceprevir,telaprevir,telaprevir,抗抑郁剂,或抗抑郁剂。这些药物与洛伐他汀的结合是禁忌的。如果不可避免地使用强CYP3A4抑制剂的短期治疗,则应在治疗过程中暂停lovastatin的治疗((see CONTRAINDICATIONS; PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions).
Gemfibrozil
The combined use of lovastatin with gemfibrozil should be avoided.
other lipid-lowering drugs (other fibrates or ≥1 g/day of niacin)
在开处方其他纤维或降低脂质剂量(≥1g/天)的烟酸中,应谨慎使用,因为这些药物在单独给予时可能会引起肌病。The benefit of further alterations in lipid levels by the combined use of lovastatin with other fibrates or niacin should be carefully weighed against the potential risks of these combinations。
环孢菌素
The use of lovastatin with cyclosporine should be avoided.
Danazol, diltiazem, dronedarone or verapamil with higher doses of lovastatin
与Danazol,Diltiazem,Dronedarone或Verapamil相关药物的患者,洛伐他汀的剂量不得每天超过20 mg。The benefits of the use of lovastatin in patients receiving danazol, diltiazem, dronedarone, or verapamil should be carefully weighed against the risks of these combinations.
Amiodarone
The dose of lovastatin should not exceed 40 mg daily in patients receiving concomitant medication with amiodarone。The combined use of lovastatin at doses higher than 40 mg daily with amiodarone should be avoided unless the clinical benefit is likely to outweigh the increased risk of myopathy. The risk of myopathy/rhabdomyolysis is increased when amiodarone is used concomitantly with higher doses of a closely related member of the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor class.
Colchicine
Cases of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis, have been reported with lovastatin coadministered with colchicine, and caution should be exercised when prescribing lovastatin with colchicine((see PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions).
Ranolazine
雷诺嗪的给药可能会增加肌病的风险,包括横纹肌溶解。在与雷诺嗪共同给药期间,可以考虑lovastatin的剂量调整。
Prescribing recommendations for interacting agents are summarized in Table VII(另请参见临床药理学,药代动力学;预防措施,药物相互作用;剂量和给药).
表VII 与肌病/横纹肌溶解的风险增加有关的药物相互作用 |
|
我nteracting Agents |
Prescribing Recommendations |
Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, e.g.: Ketoconazole 我traconazole Posaconazole Voriconazole Erythromycin Clarithromycin Telithromycin H我V protease inhibitors Boceprevir Telaprevir Nefazodone Cobicistat-containing products |
Contraindicated with lovastatin |
Gemfibrozil 环孢菌素 |
Avoid with lovastatin |
Danazol Diltiazem Dronedarone Verapamil |
Do not exceed 20 mg lovastatin daily |
Amiodarone |
Do not exceed 40 mg lovastatin daily |
葡萄柚汁 |
Avoid grapefruit juice |
肝功能障碍
Persistent increases (to more than 3 times the upper limit of normal) in serum transaminases occurred in 1.9% of adult patients who received lovastatin for at least one year in early clinical trials((请参阅不良反应). When the drug was interrupted or discontinued in these patients, the transaminase levels usually fell slowly to pretreatment levels. The increases usually appeared 3 to 12 months after the start of therapy with lovastatin, and were not associated with jaundice or other clinical signs or symptoms. There was no evidence of hypersensitivity. In the EXCEL study (参见临床药理学,临床研究),安慰剂中血清转氨酶持续增加的发生率为0.1%,在20 mg/天时为0.1%,在40 mg/天时为0.9%,lovastatin的患者在80 mg/天时为1.5%。然而,在洛伐他汀的销售后经验中,症状性肝病很少在所有剂量(请参阅不良反应).
在AFCAPS/TEXCAP中,丙氨酸氨基转移酶(ALT)或天冬氨酸氨基转移酶(AST)(AST)(>正常上限的3倍)的参与者人数在5.1年的随访中,并未显着,并不明显lovastatin和安慰剂组之间的不同(18 [0.6%]比11 [0.3%])。洛伐他汀的起始剂量为20毫克/天;在第18周,经过50%的lovastatin治疗参与者被滴定至40 mg/天。在洛伐他汀的18名参与者中,有20毫克/天的参与者发生了11个(0.7%)高程,而7个(0.7%)的高程发生,而7位则为7毫克。(0.4%)在滴定到40 mg/天的参与者中发生了高程。升高的转氨酶导致在洛伐他汀组(n = 3,304)中停用6(0.2%)参与者在安慰剂组中停止治疗(n = 3,304)(n = 3,301)。
建议在使用lovastatin进行治疗之前先获得肝酶检测,并按照临床指示重复。
There have been rare postmarketing reports of fatal and non-fatal hepatic failure in patients taking statins, including lovastatin. If serious liver injury with clinical symptoms and/or hyperbilirubinemia or jaundice occurs during treatment with lovastatin, promptly interrupt therapy. If an alternate etiology is not found do not restart lovastatin.
The drug should be used with caution in patients who consume substantial quantities of alcohol and/or have a past history of liver disease. Active liver disease or unexplained transaminase elevations are contraindications to the use of lovastatin.
据报道,洛伐他汀治疗后,已经报道了血清转氨酶的中等(少于正常上限的三倍)请参阅不良反应). These changes appeared soon after initiation of therapy with lovastatin, were often transient, were not accompanied by any symptoms and interruption of treatment was not required.
Legal Issues
There is currently no legal information available for this drug.
FDA Safety Alerts
There are currently no FDA safety alerts available for this drug.
Manufacturer Warnings
目前尚无该药物可用的制造商警告信息。
FDA Labeling Changes
There are currently no FDA labeling changes available for this drug.
Uses
lovastatin片剂USP的治疗应成为那些患有动脉粥样硬化血管疾病风险的患者多重危险因素干预的组成部分。除了饱和脂肪和胆固醇限制的饮食外,还应使用lovastatin片剂USP,作为治疗策略的一部分,以将总C和LDL-C降低到目标水平,而仅仅对饮食和其他非药理学措施的反应就不足以减少饮食和其他非药理学措施。风险。
Primary Prevention of Coronary Heart Disease
我n individuals without symptomatic cardiovascular disease, average to moderately elevated total-C and LDL-C and below average HDL-C, lovastatin tablets USP are indicated to reduce the risk of:
- 肌梗死
-Unstable angina
-Coronary revascularization procedures
((SeeCLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Clinical Studies).
Coronary Heart Disease
lovastatin片剂USP被指出会减慢冠状动脉疾病患者的冠状动脉粥样硬化进展,这是将总C和LDL-C降低到目标水平的治疗策略的一部分。
Hypercholesterolemia
治疗lipid-altering代理应该是一个component of multiple risk factor intervention in those individuals at significantly increased risk for atherosclerotic vascular disease due to hypercholesterolemia. Lovastatin tablets USP are indicated as an adjunct to diet for the reduction of elevated total-C and LDL-C levels in patients with primary hypercholesterolemia (Types IIa and IIb2), when the response to diet restricted in saturated fat and cholesterol and to other nonpharmacological measures alone has been inadequate.
2Classification of Hyperlipoproteinemias
Type |
Lipoproteins 高架 |
Lipid Elevations |
|
major |
minor |
||
我 |
乳糜微粒 |
TG |
↑→C |
我我a |
LDL |
C |
- |
我我b |
LDL, VLDL |
C |
TG |
iii(稀有) |
我DL |
C/TG |
- |
我V |
VLDL |
TG |
↑ →C |
V (rare) |
乳糜微粒, VLDL |
TG |
↑→C |
我DL = intermediate-density lipoprotein.
Adolescent Patients with Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia
Lovastatin tablets USP are indicated as an adjunct to diet to reduce total-C, LDL-C and apolipoprotein B levels in adolescent boys and girls who are at least one year post-menarche, 10 to 17 years of age, with heFH if after an adequate trial of diet therapy the following findings are present:
1。LDL-C remains >189 mg/dL or
2。LDL-C remains >160 mg/dL和:
- there is a positive family history of premature cardiovascular disease or
- 青少年患者存在两个或多个其他CVD危险因素
一般建议
Prior to initiating therapy with lovastatin, secondary causes for hypercholesterolemia (e.g., poorly controlled diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, nephrotic syndrome, dysproteinemias, obstructive liver disease, other drug therapy, alcoholism) should be excluded, and a lipid profile performed to measure total-C, HDL-C, and TG. For patients with TG less than 400 mg/dL (<4.5 mmol/L), LDL-C can be estimated using the following equation:
LDL-C = total-C – [0.2 × (TG) + HDL-C]
For TG levels >400 mg/dL (>4.5 mmol/L), this equation is less accurate and LDL-C concentrations should be determined by ultracentrifugation. In hypertriglyceridemic patients, LDL-C may be low or normal despite elevated total-C. In such cases, lovastatin tablets USP are not indicated.
The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Treatment Guidelines are summarized below:
NCEP Treatment Guidelines: LDL-C Goals and Cutpoints for Therapeutic Lifestyle Changes and Drug Therapy in Different Risk Categories |
|||
Risk Category |
LDL目标 ((mg/dL) |
LDLLevel at Which to Initiate Therapeutic Lifestyle Changes ((mg/dL) |
LDLLevel at Which to Consider Drug Therapy ((mg/dL) |
CHD†or CHD risk equivalents (10-year risk >20%) |
<100 |
≥100 |
≥130 ((100to 129: drug optional)†† |
2+ Risk factors ((10-year risk ≤20%) |
<130 |
≥130 |
10-year risk 10 to 20%: ≥130 10年风险<10%:≥160 |
0-1风险因素††† |
<160 |
≥160 |
≥190 ((160 to 189: LDL-lowering drug optional) |
†冠心病,冠心病
††Some authorities recommend use of LDL-lowering drugs in this category if an LDL-C level of <100 mg/dL cannot be achieved by therapeutic lifestyle changes. Others prefer use of drugs that primarily modify triglycerides and HDL-C, e.g., nicotinic acid or fibrate. Clinical judgment also may call for deferring drug therapy in this subcategory.
†††Almost all people with 0 to 1 risk factor have a 10-year risk <10%; thus, 10-year risk assessment in people with 0 to 1 risk factor is not necessary.
After the LDL-C goal has been achieved, if the TG is still ≥200 mg/dL, non-HDL-C (total-C minus HDL-C) becomes a secondary target of therapy. Non-HDL-C goals are set 30 mg/dL higher than LDL-C goals for each risk category.
At the time of hospitalization for an acute coronary event, consideration can be given to initiating drug therapy at discharge if the LDL-C is ≥130 mg/dL (see NCEP Guidelines above).
Since the goal of treatment is to lower LDL-C, the NCEP recommends that LDL-C levels be used to initiate and assess treatment response. Only if LDL-C levels are not available, should the total-C be used to monitor therapy.
Although lovastatin tablets USP may be useful to reduce elevated LDL-C levels in patients with combined hypercholesterolemia and hypertriglyceridemia where hypercholesterolemia is the major abnormality (Type IIb hyperlipoproteinemia), it has not been studied in conditions where the major abnormality is elevation of chylomicrons, VLDL or IDL (i.e., hyperlipoproteinemia types I, III, IV, or V).2
The NCEP classification of cholesterol levels in pediatric patients with a familial history of hypercholesterolemia or premature cardiovascular disease is summarized below:
Category |
Total-C (mg/dL) |
LDL-C(mg/dl) |
Acceptable |
<170 |
<110 |
边缘 |
170至199 |
110至129 |
高的 |
≥200 |
≥130 |
在成年期应重新评估青春期治疗的儿童,并对降低胆固醇的方案进行适当的更改,以实现LDL-C的成人目标。
历史
There is currently no drug history available for this drug.
other Information
洛伐他汀是一种从菌株中分离出来的胆固醇降低剂Aspergillus terreus。洛伐他汀口服摄入后,这是一个active lactone, is hydrolyzed to the corresponding β-hydroxyacid form. This is a principal metabolite and an inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase. This enzyme catalyzes the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonate, which is an early and rate limiting step in the biosynthesis of cholesterol.
Lovastatin is [1S-[1α(R*),3α,7β,8β(2S*,4S*),8aβ]]-1,2,3,7, 8,8a-hexahydro-3,7-dimethyl-8-[2-(tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-6-oxo-2H-pyran-2-yl)ethyl]-1-naphthalenyl 2-methylbutanoate. The empirical formula of lovastatin is C24H36o5和its molecular weight is 404.55. Its structural formula is:
洛伐他汀是一种白色、不吸湿性的晶体powder that is insoluble in water and sparingly soluble in ethanol, methanol, and acetonitrile.
Lovastatin片剂USP提供为10 mg,20 mg和40毫克片剂,用于口服。除活性成分外lovastin外,每片片剂还包含以下不活跃成分:D&C黄色10号铝制湖泊,FD&C蓝色2号铝制湖泊,乳糖无水,乳糖单水合物,镁硬石酸盐,硬晶酸盐,微晶晶体管纤维素纤维素和预凝胶玉米蛋白凝固。将丁基化羟基烷(BHA)作为防腐剂添加。
Sources
Twinrix制造商
-
Glaxosmithkline Biologicals Sa
![Twinrix(丙型肝炎和乙型肝炎(重组)疫苗)注射,悬浮液[GlaxoSmithkline生物学SA]](//www.lbxkm.com/wp-content/themes/bootstrap/assets/img/loading2.gif)
Twinrix | International Labs, Inc.
![Twinrix (Hepatitis A And Hepatitis B (Recombinant) Vaccine) Injection, Suspension [Glaxosmithkline Biologicals Sa] Twinrix(丙型肝炎和乙型肝炎(重组)疫苗)注射,悬浮液[GlaxoSmithkline生物学SA]](//www.lbxkm.com/wp-content/themes/bootstrap/assets/img/loading2.gif)
The patient should be placed on a standard cholesterol-lowering diet before receiving lovastatin tablets USP and should continue on this diet during treatment with lovastatin tablets USP (see NCEP Treatment Guidelines for details on dietary therapy). Lovastatin tablets USP should be given with meals.
Adult Patients
The usual recommended starting dose is 20 mg once a day given with the evening meal. The recommended dosing range of lovastatin is 10 to 80 mg/day in single or two divided doses; the maximum recommended dose is 80 mg/day. Doses should be individualized according to the recommended goal of therapy (see NCEP Guidelines and CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY). Patients requiring reductions in LDL-C of 20% or more to achieve their goal (see INDICATIONS AND USAGE) should be started on 20 mg/day of lovastatin tablets. A starting dose of 10 mg of lovastatin may be considered for patients requiring smaller reductions. Adjustments should be made at intervals of 4 weeks or more.
Cholesterol levels should be monitored periodically and consideration should be given to reducing the dosage of lovastatin tablets if cholesterol levels fall significantly below the targeted range.
Dosage in Patients taking Danazol, Diltiazem, Dronedarone or Verapamil
在服用Danazol,diltiazem,Dronedarone或Verapamil与lovastatin同时服用的患者中,治疗应从10 mg的lovastatin开始,不应超过20 mg/天(请参阅临床药理,药代动力学,警告,肌病/横纹肌,药物,药物,药物,药物,药物,药物,药物相互作用,药物,药物,药物互动)。
服用胺碘酮的患者剂量
我n patients taking amiodarone concomitantly with lovastatin, the dose should not exceed 40 mg/day (see WARNINGS, Myopathy/Rhabdomyolysis and PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions, Other Drug Interactions).
Adolescent Patients (10 to 17 years of age) with Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia
The recommended dosing range of lovastatin is 10 to 40 mg/day; the maximum recommended dose is 40 mg/day. Doses should be individualized according to the recommended goal of therapy (see NCEP Pediatric Panel Guidelines 4, CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, and INDICATIONS AND USAGE). Patients requiring reductions in LDL-C of 20% or more to achieve their goal should be started on 20 mg/day of lovastatin. A starting dose of 10 mg of lovastatin may be considered for patients requiring smaller reductions. Adjustments should be made at intervals of 4 weeks or more.
Concomitant Lipid-Lowering Therapy
lovastatin片剂USP单独或与胆汁酸性螯合剂一起使用时(请参阅警告,肌病/横纹肌溶解和预防措施,药物相互作用)。
肾功能不全患者的剂量
在严重肾功能不全(肌酐清除率<30 mL/min)的患者中,应仔细考虑剂量升高到20 mg/天以上,如果认为有必要进行谨慎地实施(请参阅临床药理学和警告,肌病/横纹肌溶解)。
登录到您的免费帐户